Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly create a physical or digital model of a part or product. It allows designers and engineers to quickly iterate, test, and refine their designs.
The main purpose of making prototypes is to test and validate ideas, designs, and concepts before committing to full-scale production. Here are the key objectives of creating prototypes:
1. Validation of Design:
Prototypes help in verifying that the design meets the intended requirements and specifications. This includes checking the form, fit, and function of the design.
2. Detection of Flaws and Issues:
By building and testing prototypes, potential design flaws, usability issues, and other problems can be identified and addressed early in the development process.
3. Improvement:
Prototyping allows for rapid iteration, enabling designers and engineers to refine and improve the product through successive versions.
4. Feasibility Assessment:
Prototypes can be used to evaluate the feasibility of manufacturing methods and materials, ensuring that the product can be produced efficiently and cost-effectively.
5. Risk Reduction:
By testing prototypes, companies can reduce the risk of costly errors and design changes later in the development process, leading to more successful product launches.
Although there are many methods for rapid prototyping, we primarily use CNC machining combined with skilled hand craftsmanship in our process.
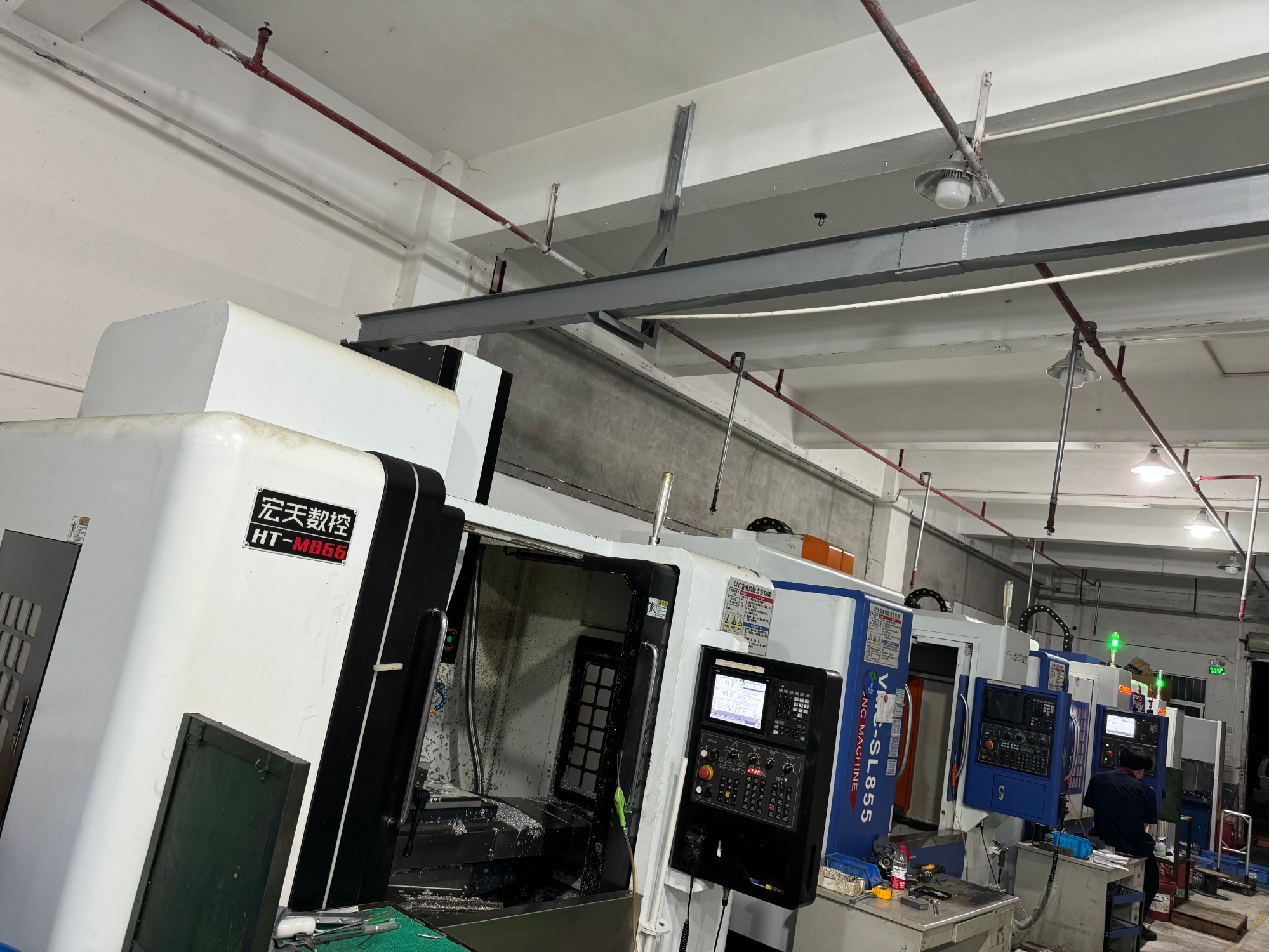
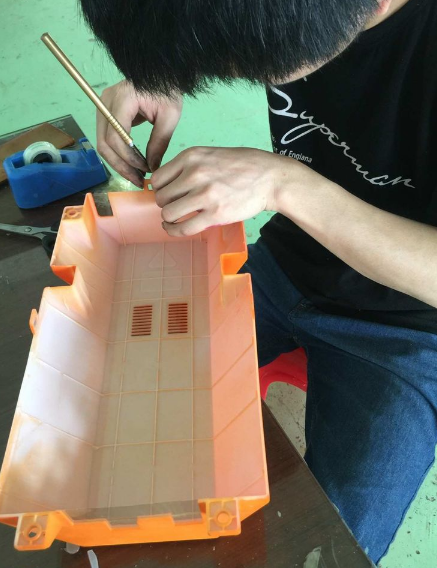



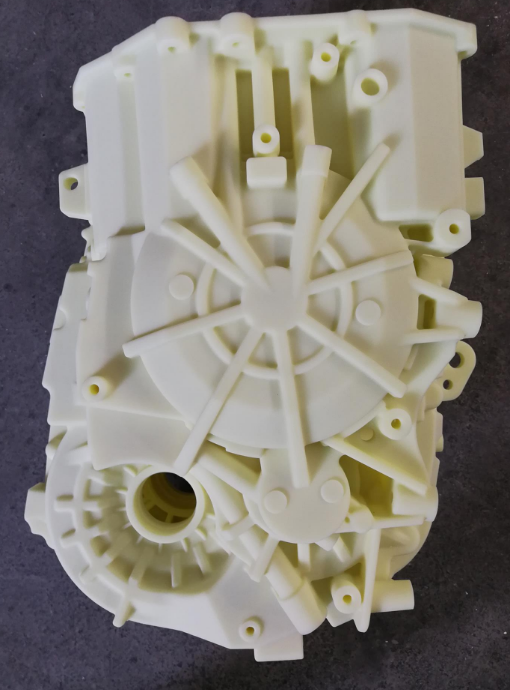
The main purpose of making prototypes is to test and validate ideas, designs, and concepts before committing to full-scale production. Here are the key objectives of creating prototypes:
1. Validation of Design:
Prototypes help in verifying that the design meets the intended requirements and specifications. This includes checking the form, fit, and function of the design.
2. Detection of Flaws and Issues:
By building and testing prototypes, potential design flaws, usability issues, and other problems can be identified and addressed early in the development process.
3. Improvement:
Prototyping allows for rapid iteration, enabling designers and engineers to refine and improve the product through successive versions.
4. Feasibility Assessment:
Prototypes can be used to evaluate the feasibility of manufacturing methods and materials, ensuring that the product can be produced efficiently and cost-effectively.
5. Risk Reduction:
By testing prototypes, companies can reduce the risk of costly errors and design changes later in the development process, leading to more successful product launches.
Although there are many methods for rapid prototyping, we primarily use CNC machining combined with skilled hand craftsmanship in our process.







